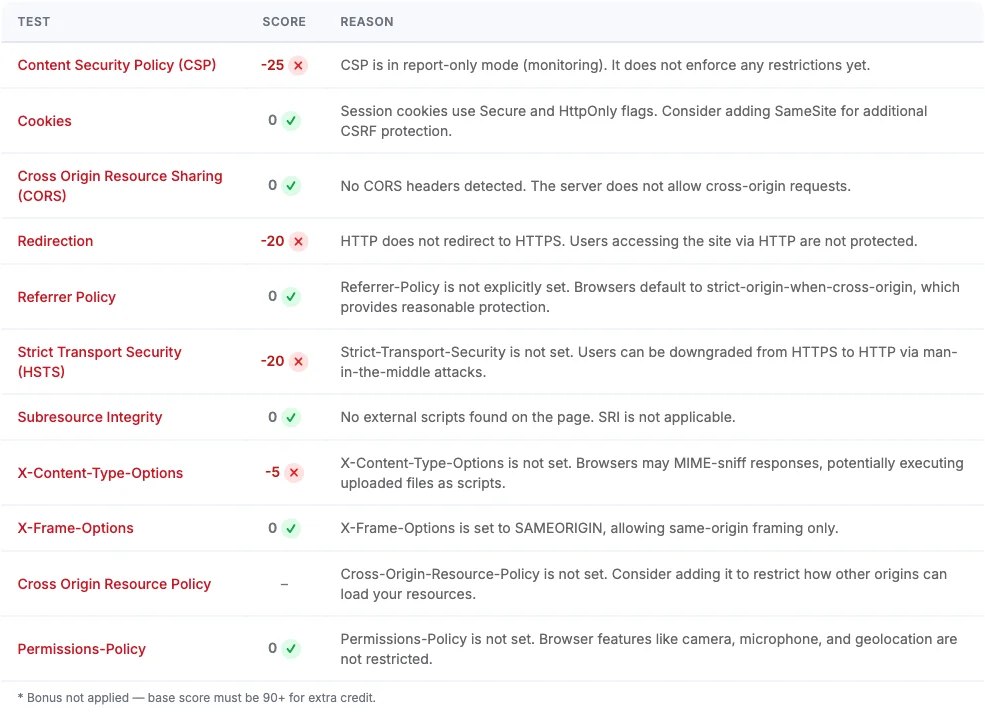
HTTP security headers are directives sent by a web server that tell browsers how to behave when handling a site's content. They form a critical defense layer against cross-site scripting (XSS), clickjacking, protocol downgrade attacks, and data injection.
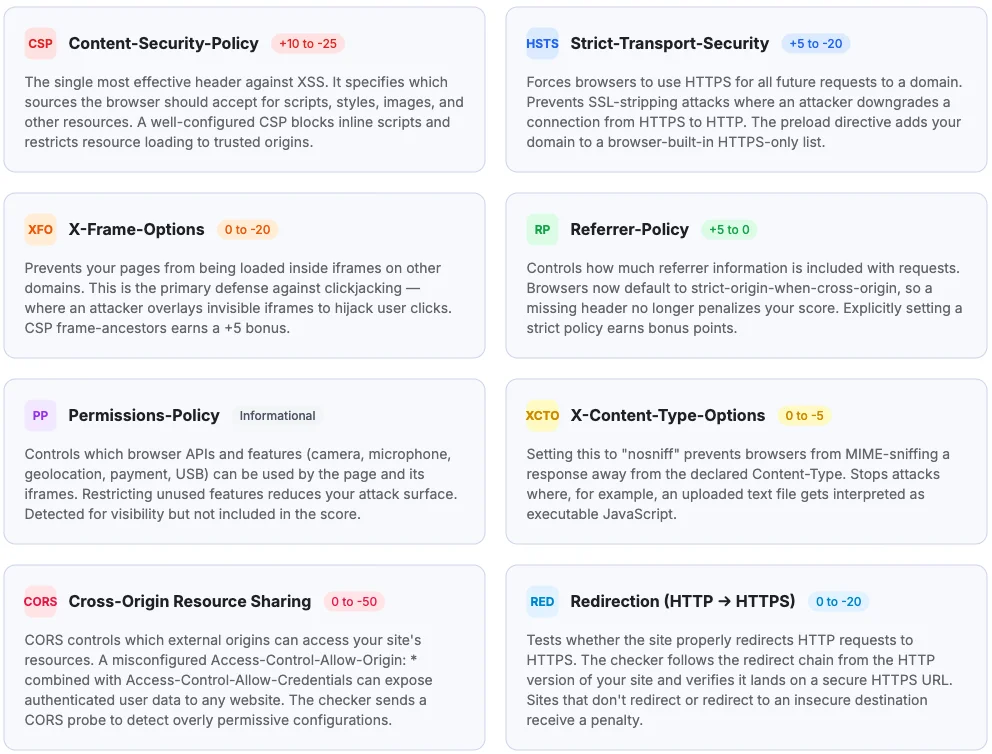
CSP
Content-Security-Policy
+10 to -25The single most effective header against XSS. It specifies which sources the browser should accept for scripts, styles, images, and other resources. A well-configured CSP blocks inline scripts and restricts resource loading to trusted origins.
HSTS
Strict-Transport-Security
+5 to -20Forces browsers to use HTTPS for all future requests to a domain. Prevents SSL-stripping attacks where an attacker downgrades a connection from HTTPS to HTTP. The preload directive adds your domain to a browser-built-in HTTPS-only list.
XFO
X-Frame-Options
0 to -20Prevents your pages from being loaded inside iframes on other domains. This is the primary defense against clickjacking — where an attacker overlays invisible iframes to hijack user clicks. CSP frame-ancestors earns a +5 bonus.
RP
Referrer-Policy
+5 to 0Controls how much referrer information is included with requests. Browsers now default to strict-origin-when-cross-origin, so a missing header no longer penalizes your score. Explicitly setting a strict policy earns bonus points.
PP
Permissions-Policy
InformationalControls which browser APIs and features (camera, microphone, geolocation, payment, USB) can be used by the page and its iframes. Restricting unused features reduces your attack surface. Detected for visibility but not included in the score.
XCTO
X-Content-Type-Options
0 to -5Setting this to "nosniff" prevents browsers from MIME-sniffing a response away from the declared Content-Type. Stops attacks where, for example, an uploaded text file gets interpreted as executable JavaScript.
CORS
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing
0 to -50CORS controls which external origins can access your site's resources. A misconfigured Access-Control-Allow-Origin: * combined with Access-Control-Allow-Credentials can expose authenticated user data to any website. The checker sends a CORS probe to detect overly permissive configurations.
RED
Redirection (HTTP → HTTPS)
0 to -20Tests whether the site properly redirects HTTP requests to HTTPS. The checker follows the redirect chain from the HTTP version of your site and verifies it lands on a secure HTTPS URL. Sites that don't redirect or redirect to an insecure destination receive a penalty.
SRI
Subresource Integrity
+5 to -50SRI ensures that third-party scripts and stylesheets haven't been tampered with by requiring cryptographic hashes in the integrity attribute. If a CDN or external host is compromised, the browser refuses to execute resources that don't match their expected hash.
CORP
Cross-Origin-Resource-Policy
0 to -5Prevents other sites from loading your resources (images, scripts, etc.) without permission. Setting CORP to "same-origin" or "same-site" blocks unauthorized cross-origin embedding, protecting against Spectre-style side-channel attacks and data leaks.
info
Cross-Origin Isolation (COOP & COEP)
InformationalCOOP (Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy) isolates your window from cross-origin popups. COEP (Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy) ensures all embedded resources are explicitly shared. Together they enable cross-origin isolation for advanced APIs like SharedArrayBuffer. These are analyzed for visibility but not included in the score.