Dependabot is GitHub’s built-in dependency security tool. It’s free for every GitHub repository, public or private, and requires no external services or API tokens.
According to the 2025 GitHub Octoverse report, Dependabot is the most widely adopted SCA tool among open-source projects.
It operates across three layers: alerts tell you when a dependency has a known vulnerability, security updates open PRs to fix those vulnerabilities, and version updates keep all your dependencies current. Over 846,000 repositories have Dependabot configured, with 137% year-over-year adoption growth according to the 2025 GitHub Octoverse report.
GitHub acquired the original Dependabot project in 2019 and integrated it directly into the platform. It now covers 30+ package ecosystems and draws from the GitHub Advisory Database (28,000+ reviewed advisories).
What is Dependabot?
Dependabot monitors your repository’s dependency manifests and lock files. When a new vulnerability appears in the GitHub Advisory Database or a newer package version is released, Dependabot opens a pull request with the update.
For security fixes, it upgrades to the minimum patched version (not the latest) to minimize the risk of breaking changes. Each PR includes a compatibility score showing the CI pass rate from public repositories that applied the same update.
Keeps all dependencies current on a configurable schedule. Supports daily, weekly, monthly, or cron-based timing.
Group updates by name pattern, dependency type, or semver level to reduce PR noise.
Key features
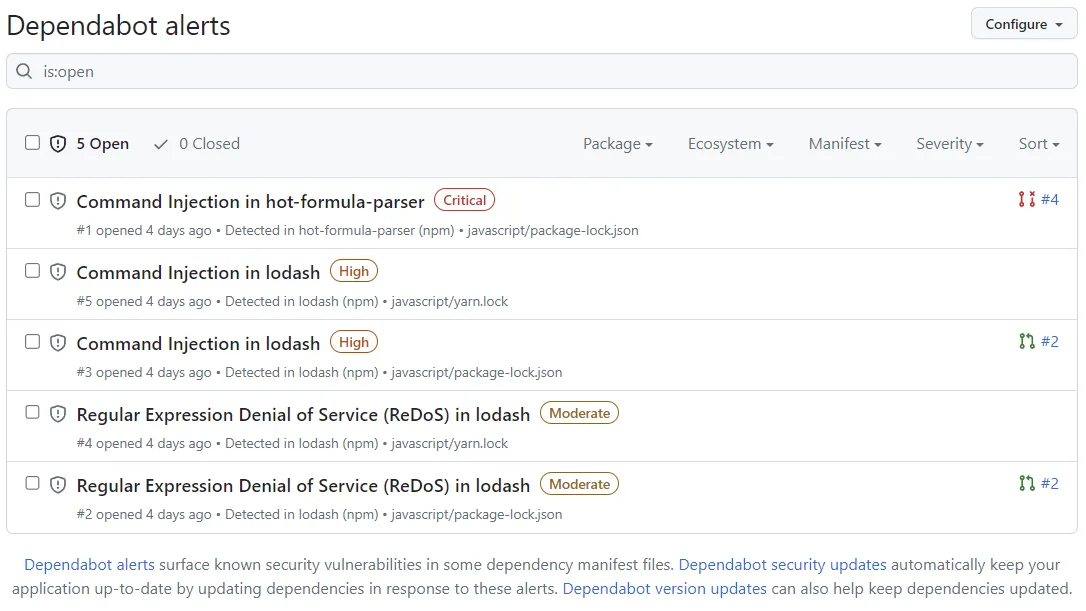
Vulnerability alerts
When a dependency in your repository matches a vulnerability in the GitHub Advisory Database, Dependabot creates an alert. Each alert includes the CVE details, severity rating, affected versions, and patched version.
You can filter by ecosystem, severity, package name, and scope (development vs. production).
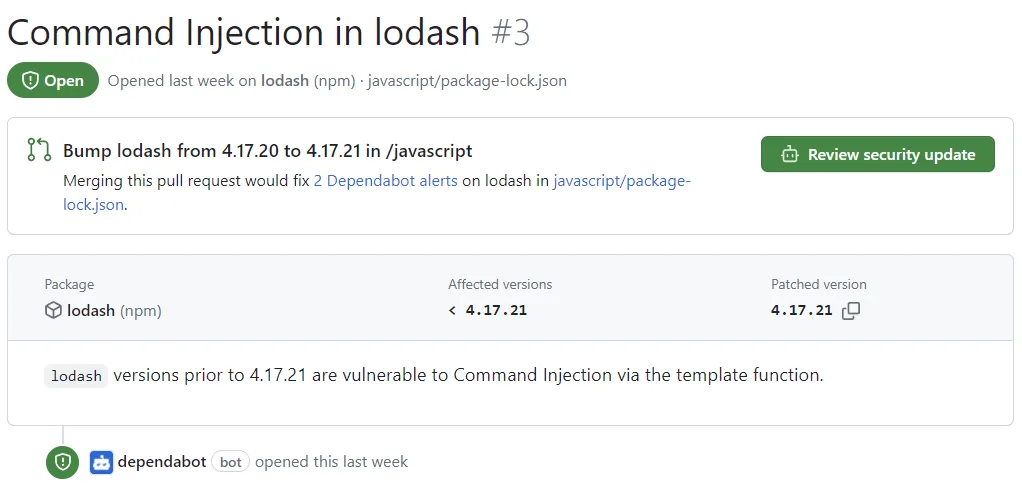
Security updates
When a vulnerability has a fix, Dependabot creates a PR that bumps the dependency to the minimum patched version. The PR includes release notes, changelog entries, and a compatibility score.
Grouped security updates bundle multiple fixes per ecosystem into a single PR.
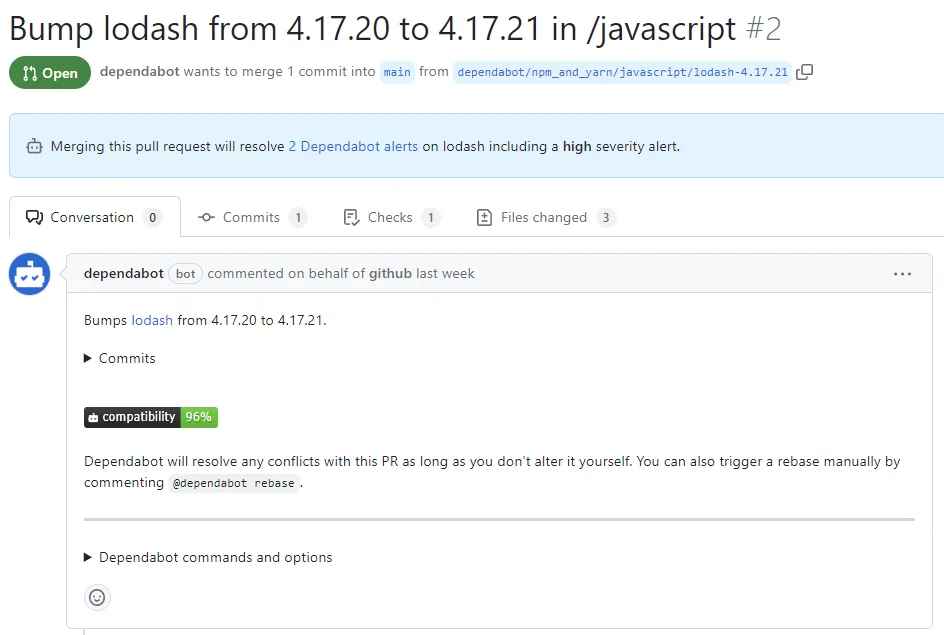
Version updates
Version updates keep dependencies current regardless of vulnerability status. Configure them through .github/dependabot.yml with scheduling options (daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, semiannually, yearly, or cron expressions) and grouping rules.
Grouped updates
Group related dependency updates into fewer PRs. You can group by:
- Dependency name patterns –
"@aws-sdk/*"or"eslint*" - Dependency type – production vs. development
- Semver level – patch, minor, major
- Cross-ecosystem – combine updates from npm, pip, and Docker into one PR (GA since July 2025)
Cooldown periods
Delay updates for newly released versions. Set a default cooldown (1-90 days) and override per semver level.
This avoids updating to day-zero releases that might have undiscovered issues.
Auto-triage rules
GitHub provides preset rules that auto-dismiss low-impact alerts on development dependencies. You can create custom rules that filter by severity, package name, and CWE to reduce noise while keeping coverage on what matters.
Setup
.github/dependabot.yml to enable version updates. Specify which ecosystems to track and how often to check.dependabot/fetch-metadata to auto-merge low-risk patch and minor updates after tests pass.Basic configuration
version: 2
updates:
- package-ecosystem: "npm"
directory: "/"
schedule:
interval: "weekly"
day: "monday"
time: "06:00"
timezone: "America/New_York"
open-pull-requests-limit: 10
groups:
production-deps:
dependency-type: production
update-types: ["minor", "patch"]
dev-deps:
dependency-type: development
- package-ecosystem: "docker"
directory: "/"
schedule:
interval: "weekly"
- package-ecosystem: "github-actions"
directory: "/"
schedule:
interval: "weekly"
Auto-merge with GitHub Actions
name: Dependabot auto-merge
on: pull_request
permissions:
contents: write
pull-requests: write
jobs:
auto-merge:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: github.actor == 'dependabot[bot]'
steps:
- name: Fetch Dependabot metadata
id: metadata
uses: dependabot/fetch-metadata@v2
with:
github-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Auto-merge minor and patch updates
if: steps.metadata.outputs.update-type == 'version-update:semver-patch' || steps.metadata.outputs.update-type == 'version-update:semver-minor'
run: gh pr merge --auto --squash "$PR_URL"
env:
PR_URL: ${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url }}
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
Supported ecosystems
Dependabot supports 30+ package ecosystems:
| Ecosystem | Config Value | Manifest Files |
|---|---|---|
| JavaScript (npm) | npm | package.json, package-lock.json |
| JavaScript (yarn) | npm | package.json, yarn.lock |
| JavaScript (pnpm) | npm | package.json, pnpm-lock.yaml (auto-detected) |
| JavaScript (Bun) | bun | package.json, bun.lock |
| Python (pip) | pip | requirements.txt, setup.py, pyproject.toml |
| Python (uv) | uv | pyproject.toml, uv.lock |
| Java (Maven) | maven | pom.xml |
| Java (Gradle) | gradle | build.gradle, build.gradle.kts |
| Ruby | bundler | Gemfile, Gemfile.lock |
| PHP | composer | composer.json, composer.lock |
| .NET | nuget | packages.config, *.csproj |
| Go | gomod | go.mod, go.sum |
| Rust | cargo | Cargo.toml, Cargo.lock |
| Swift | swift | Package.swift, Package.resolved |
| Dart | pub | pubspec.yaml, pubspec.lock |
| Elixir | mix | mix.exs, mix.lock |
| Docker | docker | Dockerfile |
| Terraform | terraform | .tf, .terraform.lock.hcl |
| GitHub Actions | github-actions | .yml, .yaml workflows |
| Helm | helm | Chart.yaml |
When to use Dependabot
Dependabot is the default choice for any GitHub-hosted repository. It’s free, requires minimal configuration, and handles the most common dependency update scenarios.
Strengths:
- Free for all GitHub repositories, no limits
- Zero-setup for security alerts; one YAML file for version updates
- 30+ ecosystems covering virtually every major language
- Compatibility scores based on public CI pass rates
- Grouped updates reduce PR noise across and within ecosystems
- Auto-triage rules minimize alert fatigue
Limitations:
- GitHub only. If your repos are on GitLab, Bitbucket, or Azure DevOps, use Renovate or Snyk Open Source instead
- No proprietary vulnerability database; relies on the GitHub Advisory Database
- No license compliance features (pair with FOSSA or Black Duck)
- No reachability analysis
How it compares:
| vs. | Key difference |
|---|---|
| Renovate | Renovate supports GitLab, Bitbucket, and Azure DevOps. More advanced scheduling, regex managers, and shared presets. Dependabot is simpler and GitHub-native. |
| Snyk Open Source | Snyk has a larger vulnerability database, reachability analysis, and automated fix PRs across multiple platforms. Dependabot is free and simpler for GitHub-only teams. |
| Grype | Grype scans containers and SBOMs but doesn’t create update PRs. Different tools for different jobs. |
To understand how Dependabot fits into a broader security pipeline, read our guides on SCA in CI/CD and supply chain attacks.